Introduction to Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to explore the relationship between a dependent variable (also known as the outcome variable or response variable) and one or more independent variables (also known as predictor or explanatory variables). The primary goal of regression analysis is to identify the nature and strength of the relationship between the variables and make predictions based on that relationship.
The most commonly used type of regression analysis is linear regression, where a straight line is used to model the relationship between two variables. The relationship between the variables is expressed in terms of a mathematical equation, known as a regression equation or a linear equation.
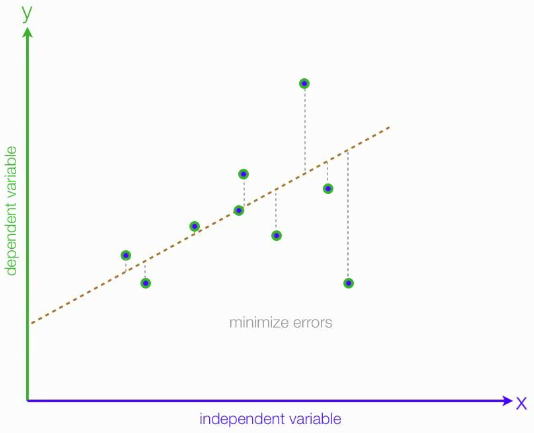
The regression equation is derived by finding the line that best fits the data points. This line is called the line of best fit or the regression line. The regression line is determined by minimizing the sum of the squared differences between the observed values of the dependent variable and the predicted values of the dependent variable based on the independent variable.
There are several types of regression analysis, including linear regression, logistic regression, and multiple regression. Linear regression is the most commonly used type of regression analysis, and it is used to model a linear relationship between the dependent variable and one or more independent variables.